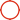
Water inlet treatment method for screw air compressor head:
In the daily use of screw air compressors, improper use can lead to water ingress, resulting in abnormal noise, lubrication system failure, abnormal pressure, abnormal discharge and drainage temperature, pressure gauge jumping, and reduced displacement of the air compressor. To prevent water from entering the screw air compressor, it is necessary to carefully follow the daily maintenance procedures.
(1) The air compressor has abnormal noise
1. There is a noise inside the cylinder
① Foreign objects or broken valve pieces falling into the cylinder, remove foreign objects or broken valve pieces;
② Excessive wear of piston rings, causing impact in the ring groove during operation, replacement of piston rings;
③ The connecting rod large end bearing, small end bushing, and piston cross hole are excessively worn and should be replaced;
④ If the top of the piston collides with the cylinder head, the gap should be adjusted;
⑤ There is water in the cylinder.
2. There is a noise inside the valve
① The intake and exhaust valve groups are not tightly compressed, and the valve chamber square cover fastening nuts should be tightened:;
② The bolts and nuts of the air valve are loose, tighten the nuts;
③ Damaged valve spring, replace it in a timely manner;
④ The gap between the valve disc and the valve cover is too large. Adjust the gap and replace the valve disc if necessary
3. There is a noise inside the crankcase
① The flywheel is not tightened or the key fit is too loose, it should be tightened;
② The connecting rod bolts are not tightened, tighten them;
③ Excessive wear of connecting rod bearings, replace with new bearings;
④ The main bearing is damaged, replace the bearing;
⑤ The oil deflector on the crankshaft is loose, replace it with a new one.
(2) Lubrication system malfunction
1. Lubricating oil is too dirty, clean lubricating oil should be replaced;
2. Oil level too high or too low, adjust the oil level to the specified range
3. The oil grade is incorrect, and the oil should be changed according to the instructions:
4. The oil needle is broken and should be replaced;
(3) Abnormal pressure at all levels (low or high)
1. The valve plate or spring of the intake and exhaust valves is damaged or leaking, and should be replaced;
2. The air filter is severely clogged and should be cleaned;
3. There is dirt or air leakage on the valve seats of the intake and exhaust valves, and the dirt should be removed;
4. Repair any leaks in the air duct or cooler;
5. The piston ring and cylinder are severely worn and leaking, and should be replaced.
(4) Excessive exhaust temperature or cooling water discharge temperature (referring to water-cooled)
1. Brushing the cylinder causes it to overheat, repair the cylinder and piston;
2. Cooling water path blockage, cylinder, cylinder head, or cooler with excessive accumulation of scale or blockage, remove scale or blockage;
3. Insufficient cooling water volume, increase cooling water flow rate;
4. Leakage of exhaust valve or valve spring, damage to valve plate, replacement of damaged parts;
5. Charcoal deposits on the intake and exhaust valves, causing blockages in the gas channel. Clean up the deposits.
(5) Exhaust pressure gauge jumping
1. Check if the intake and exhaust valve plates or springs are stuck during maintenance;
2. The pressure gauge is damaged, replace it;
3. There is foreign object in the instrument pipeline. Clean and blow off.
(6) Reduced exhaust volume
1. Air valve leakage, grinding repair or replacement with new parts;
2. If the speed of the air compressor is too low than the rated speed, check the circuit voltage and frequency for maintenance or replace the motor;
3. Air filter blockage, air leakage in the air duct, dust removal under the filter, and pipeline repair;
4. Excessive clearance at the top dead center of the piston, reducing cylinder gasket and reducing clearance volume;
5. The piston ring and cylinder are severely worn and leaking, and should be replaced.
(4) Excessive exhaust temperature or cooling water discharge temperature (referring to water-cooled)
1. Brushing the cylinder causes it to overheat, repair the cylinder and piston;
2. Cooling water path blockage, cylinder, cylinder head, or cooler with excessive accumulation of scale or blockage, remove scale or blockage;
3. Insufficient cooling water volume, increase cooling water flow rate;
4. Leakage of exhaust valve or valve spring, damage to valve plate, replacement of damaged parts;
5. Charcoal deposits on the intake and exhaust valves, causing blockages in the gas channel. Clean up the deposits.
(5) Exhaust pressure gauge jumping
1. Check if the intake and exhaust valve plates or springs are stuck during maintenance;
2. The pressure gauge is damaged, replace it;
3. There is foreign object in the instrument pipeline. Clean and blow off.
(6) Reduced exhaust volume
1. Air valve leakage, grinding repair or replacement with new parts;
2. If the speed of the air compressor is too low than the rated speed, check the circuit voltage and frequency for maintenance or replace the motor;
3. Air filter blockage, air leakage in the air duct, dust removal under the filter, and pipeline repair;
4. Excessive clearance at the top dead center of the piston, reducing cylinder gasket and reducing clearance volume;
5. Excessive wear on piston rings, oil scraper rings, and cylinders, replacement of worn parts